The Complete Guide to Tax Implications of U.S. Stock Investments
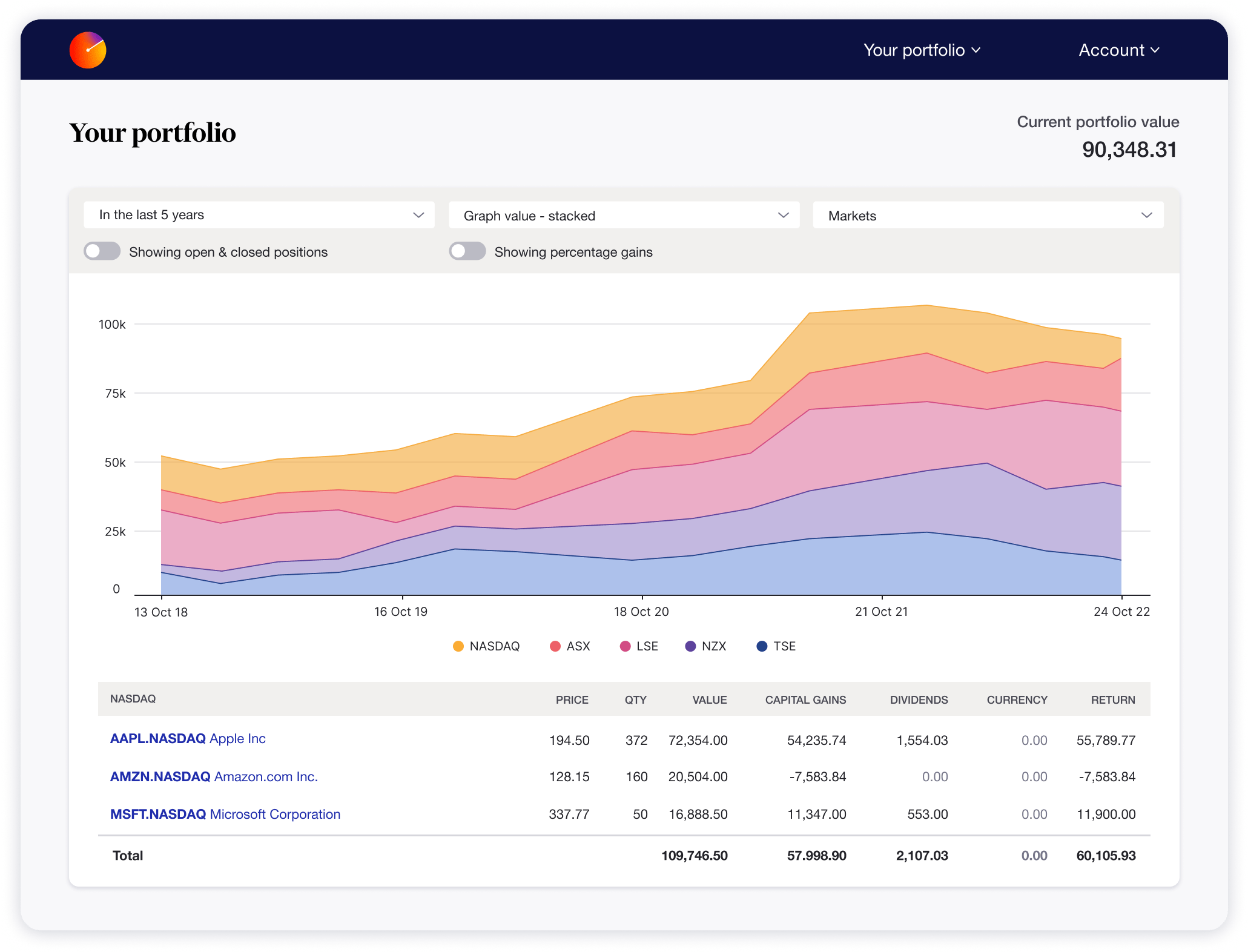
Table of Contents
Introduction
How U.S. Stock Investments Are Taxed
Key Tax Forms You’ll Encounter
Tax Rates on Capital Gains & Dividends
Special Considerations for Non‑U.S. Investors
Tax‑Advantaged Accounts in the U.S.
International Tax Treaties & Reporting Rules
Comparison Table: Tax Types & Rates
Which Is Right for You?
Practical Tax Planning Tips
Risk Disclaimer
CTA: Compare Investment Platforms / Check Current Rates
Author Bio
1. Introduction
Investing in U.S. stocks can be one of the most effective ways to build long‑term wealth. But understanding taxes is critical to keeping more of your gains. Whether you’re a U.S. resident or an international investor, the tax implications vary significantly — and missing key rules can lead to unexpected bills or even penalties.
This comprehensive guide explains how U.S. stock investments are taxed, links directly to official government sources, and helps you make smarter decisions while minimizing tax liabilities.
2. How U.S. Stock Investments Are Taxed
When you invest in U.S. stocks, your tax exposure normally arises in three primary areas:
Capital Gains Tax — tax on profit when you sell a stock
Dividend Income Tax — tax on dividends you receive
Withholding Tax (for non‑U.S. investors) – automatic tax deducted on U.S. source income
Capital Gains
When you sell a stock for more than you paid, you realize a capital gain. The IRS treats this gain as taxable income. Depending on how long you held the investment, it can be:
Short‑Term Capital Gains (held 1 year or less) — taxed at ordinary income tax rates
Long‑Term Capital Gains (held over 1 year) — taxed at preferential rates
For official IRS guidance, see IRS Topic No. 409 — Capital Gains and Losses: https://www.irs.gov/taxtopics/tc409
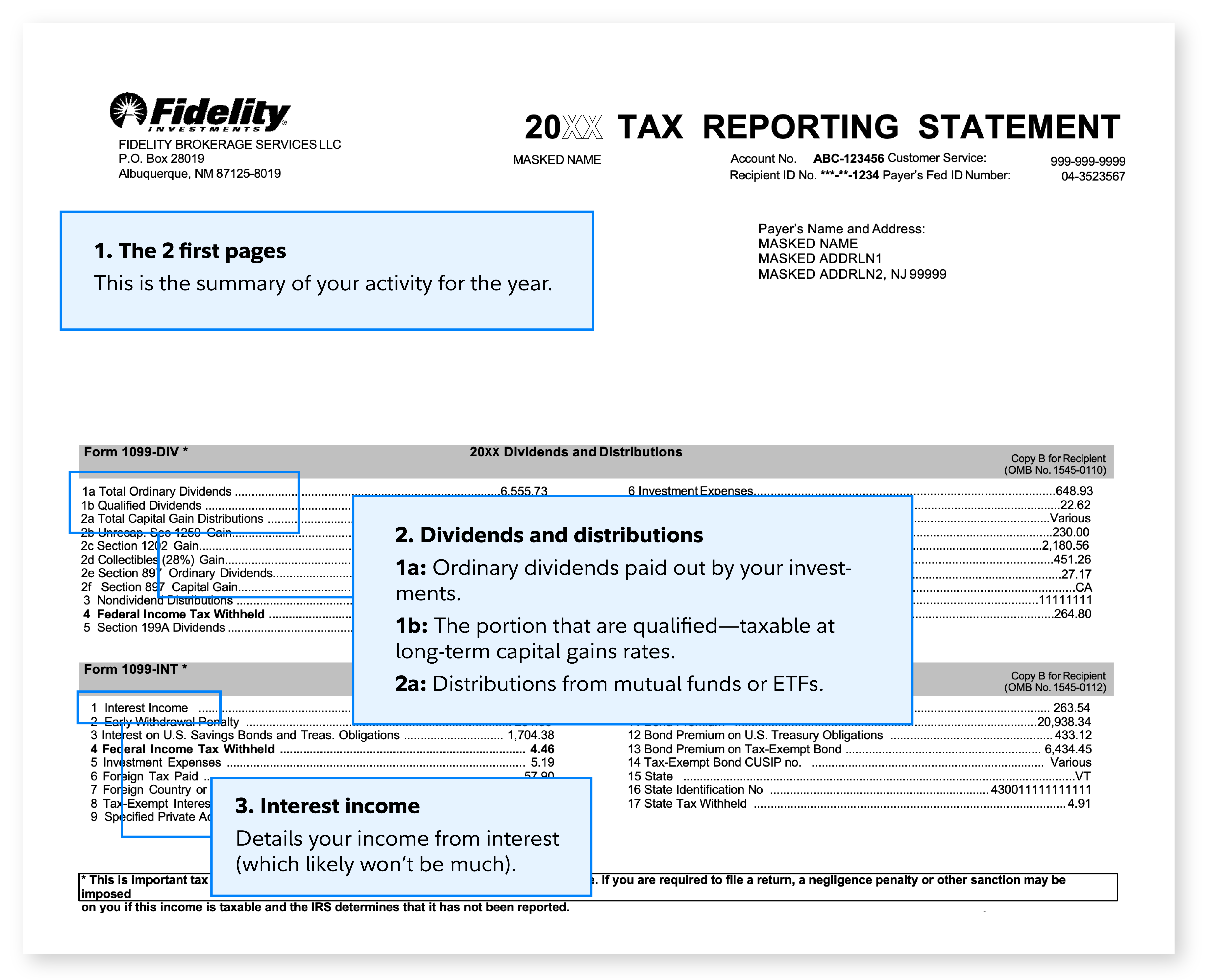
3. Key Tax Forms You’ll Encounter
Here are the key tax forms associated with stock investing:
Form 1099‑B – reports proceeds from stock sales
Form 1099‑DIV – reports dividends and distributions
Form W‑8BEN – for non‑U.S. investors to claim reduced withholding per tax treaties
Official forms can be accessed at the IRS Forms & Publications page:
https://www.irs.gov/forms‑instructions
4. Tax Rates on Capital Gains & Dividends
Understanding tax rates is essential:
For U.S. Residents
| Income Type | Tax Rate (2025) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Short‑Term Capital Gains | Ordinary tax rates (10–37%) | Same as regular income tax |
| Long‑Term Capital Gains | 0%, 15%, or 20% | Based on taxable income |
| Qualified Dividends | 0%, 15%, or 20% | Must meet holding period rules |
| Non‑Qualified Dividends | Ordinary rates | Taxed as regular income |
IRS Reference (Capital Gains & Qualified Dividends):
https://www.irs.gov/taxtopics/tc409
5. Special Considerations for Non‑U.S. Investors
Non‑U.S. shareholders face different rules:
Withholding Tax — typically 30% on U.S. dividends
May be reduced through tax treaties
No U.S. capital gains tax on stocks if no U.S. business presence
Must file Form W‑8BEN with brokers
See IRS rules for nonresident aliens here:
https://www.irs.gov/individuals/international‑taxpayers/nonresident‑aliens
6. Tax‑Advantaged Accounts in the U.S.
Investing through special U.S. accounts may defer or eliminate tax:
| Account Type | Tax Treatment | Available to Non‑U.S. Investors? |
|---|---|---|
| 401(k) | Tax‑deferred | No |
| Traditional IRA | Tax‑deferred | Depends on residency |
| Roth IRA | Tax‑free on gains | Depends on residency |
| 529 College Plan | Tax‑free for qualified expenses | Generally yes |
Learn more at IRS Publication 590:
https://www.irs.gov/publications/p590a
7. International Tax Treaties & Reporting Rules
The U.S. has treaties with numerous countries that may reduce withholding tax on dividends. To benefit:
Submit Form W‑8BEN
Provide your taxpayer ID (if required)
Check specific treaty provisions
For the latest treaties and rates, consult the Tax Treaty Tables:
https://www.irs.gov/individuals/international‑taxpayers/tax‑treaty‑tables

8. Comparison Table: Tax Types & Rates
| Tax Feature | U.S. Resident | Non‑U.S. Investor |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Gains Tax | Yes (short & long) | Often No* |
| Dividend Tax | Qualified/Non‑Qualified | Withholding Tax |
| Reporting Required | Yes | Yes |
| Withholding Relief via Treaty | N/A | Yes (with Form W‑8BEN) |
| Tax Forms | 1099 series | W‑8BEN + 1040NR (if filing) |
* Exceptions may apply if agent/broker handles differently or if investor has U.S. PE.
9. Which Is Right for You?
If You’re a U.S. Resident:
✔ Focus on holding stocks long‑term for lower tax rates.
✔ Use tax‑advantaged accounts where possible (IRA, 401(k)).
✔ Track cost basis carefully to calculate gains correctly.
If You’re a Non‑U.S. Investor:
✔ Submit Form W‑8BEN to reduce withholding.
✔ Understand your own country’s tax system — gains may be taxed locally.
✔ Don’t assume capital gains taxes are automatic; in many cases they are not — but always confirm with a tax advisor.
10. Practical Tax Planning Tips
✔ Track holding periods — to qualify for long‑term treatment.
✔ Harvest tax losses — offset gains by realizing losses.
✔ Consult a CPA or tax attorney knowledgeable in U.S. and international tax.
✔ Use reliable investment platforms that provide accurate tax documentation.
11. Risk Disclaimer
Disclaimer: This article is educational only and not financial or tax advice. Tax laws change frequently. Your personal tax situation may vary. Consult a qualified tax professional or certified public accountant before making investment decisions or interpreting your tax obligations.
12. Call‑to‑Action
👉 Compare Investment Platforms — find one that offers robust tax reporting and supports international investors.
👉 Check Current Rates — dividend withholding and capital gains tax brackets change; verify with official IRS publications or your tax professional.
13. About the Author
Azka – Financial Enthusiast
Azka is a finance content specialist passionate about helping investors understand the complexities of international markets and tax systems. With a focus on clarity and accuracy, Azka bridges finance concepts and real‑world decision‑making. Connect with more of Azka’s insights on financial literacy, investing, and global tax trends.

